Webhooks
Webhooks allow your system to receive real-time event notifications from Qwiet. After you register a webhook endpoint, Qwiet sends signed payloads whenever subscribed events occur. Your server must validate the signature and process the event payload securely.
Prerequisites
Before you configure a webhook:
-
Ensure that your server exposes an active HTTP endpoint that accepts POST requests.
-
Implement HMAC verification on your endpoint. All webhook notifications from Qwiet are signed, and verifying the signature ensures the integrity and authenticity of the payload.
-
Decide whether to use your own shared secret or the system-generated secret.
-
Ensure you have the relevant role to set up the webhook.
Webhook event headers
Every webhook request includes the following headers:
| Header | Description |
|---|---|
X-SL-Signature | HMAC signature in the format v1=<hex_signature> |
X-SL-Timestamp | Unix timestamp of the event |
X-SL-Webhook-Delivery-ID | Unique UUID for the delivery attempt |
X-SL-Event | Name of the event triggered, for example, scan.finished |
Configure the webhook
To configure a webhook in your Qwiet account, complete the following steps:
-
Log in to your Qwiet account.
-
Navigate to Organization → Settings → Webhooks.
-
In the Webhooks section, do the following:
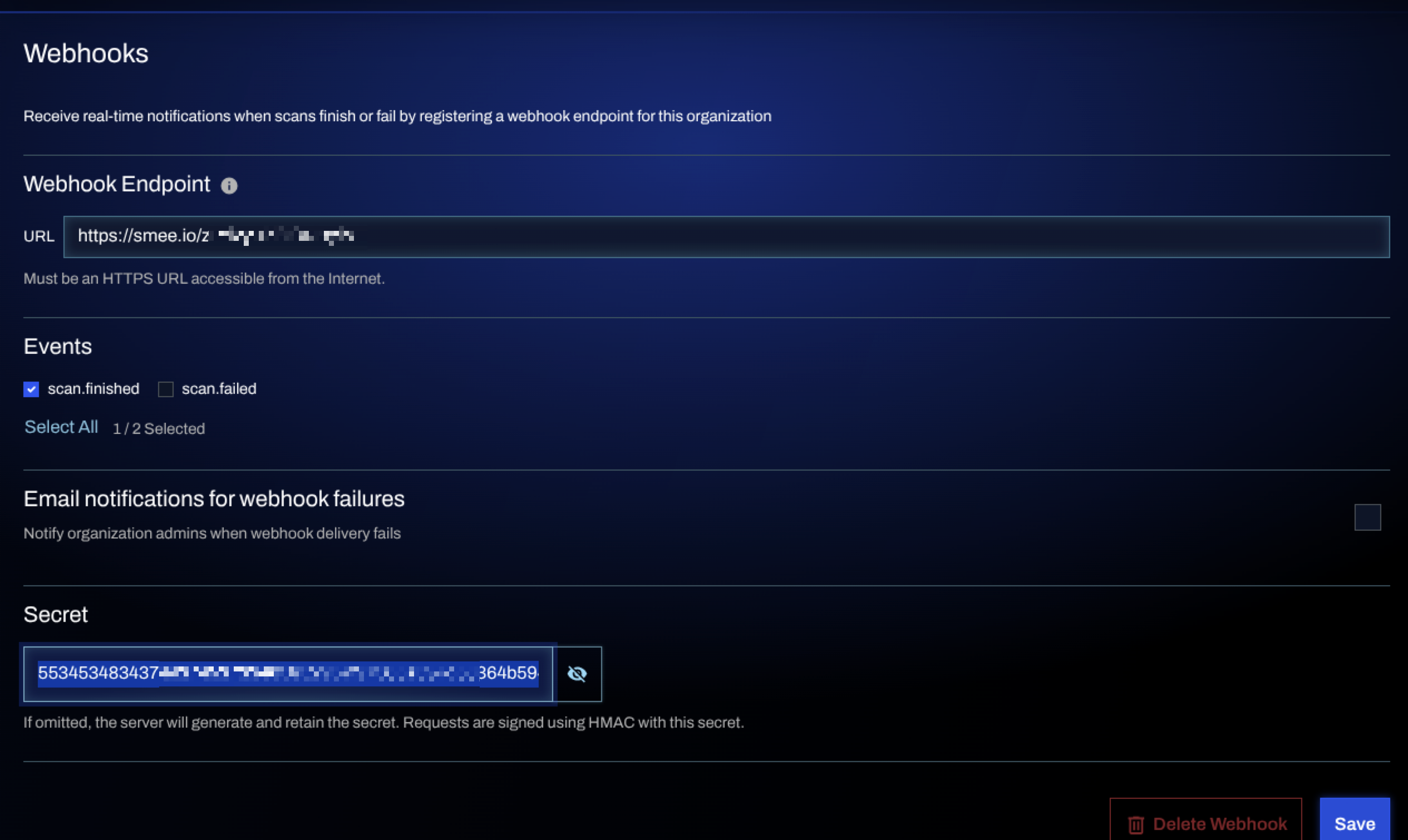
-
Specify the webhook URL.
-
Select the event types you want to subscribe to.
-
(Optional) Enable email notifications to receive alerts for failed deliveries.
-
Specify your own Secret or leave the field blank for Qwiet to generate the secret automatically when saving.
-
-
Click Save.
Webhook workflow
When a subscribed event occurs, Qwiet sends a signed POST request to your webhook URL. The request includes headers, such as the event name, timestamp, signature, and a unique delivery ID. Your endpoint must verify the signature before processing the payload.
If the delivery fails and email notifications are enabled, your organization’s admin receives an alert with details of the failure. The admin must ensure the webhook endpoint is reachable and responding correctly.
Example: Go webhook receiver
Before configuring a webhook, ensure that your server exposes an active endpoint that can validate incoming payloads. All webhook requests sent from Qwiet are signed using HMAC, which enables your server to verify that the request originated from Qwiet and that the payload has not been tampered with. To process webhooks securely, your server must implement signature verification using the shared secret. You can use a secret that is already integrated into your handler or copy the system-generated secret when creating the webhook.
For testing, you can also use services such as Beeceptor to receive webhook payloads; however, these services do not perform signature validation.
The following example shows a simple Go server that performs HMAC verification:
package main
import (
"crypto/hmac"
"crypto/sha256"
"encoding/hex"
"fmt"
"io"
"log"
"net/http"
)
const sharedSecret = "my-test-secret" // hex string or raw string depending on your setup
func verifyHMAC(timestamp, rawBody, receivedSig string) bool {
message := fmt.Sprintf("v1:%s:%s", timestamp, rawBody)
mac := hmac.New(sha256.New, []byte(sharedSecret))
mac.Write([]byte(message))
expectedSig := hex.EncodeToString(mac.Sum(nil))
// Format: "v1=<hex>"
return hmac.Equal([]byte("v1="+expectedSig), []byte(receivedSig))
}
func webhookHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
timestamp := r.Header.Get("X-SL-Timestamp")
signature := r.Header.Get("X-SL-Signature")
bodyBytes, err := io.ReadAll(r.Body)
if err != nil {
log.Printf("error reading body: %v", err)
http.Error(w, "cannot read body", http.StatusBadRequest)
return
}
rawBody := string(bodyBytes)
// For demo/debugging only, don't log in production code
log.Println("Received payload:", rawBody)
log.Println("Received signature:", signature)
log.Println("Received timestamp:", timestamp)
if verifyHMAC(timestamp, rawBody, signature) {
log.Println("HMAC verified")
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusOK)
w.Write([]byte("Signature valid"))
} else {
log.Println("Invalid signature")
http.Error(w, "Invalid signature", http.StatusUnauthorized)
}
}
func main() {
http.HandleFunc("/webhook", webhookHandler)
log.Println("Listening on :8182")
log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe(":8182", nil))
}
Example event payload
When a subscribed event occurs, Qwiet sends an HTTP POST request to the endpoint you have configured. The following example shows the headers and payload for a scan.finished event.
headers:
{
"user-agent": "Go-http-client/2.0",
"content-length": "305",
"accept-encoding": "gzip",
"content-type": "application/json",
"x-forwarded-for": "34.211.10.26",
"x-forwarded-host": "webhook-mock.free.beeceptor.com",
"x-forwarded-proto": "https",
"x-sl-event": "scan.finished",
"x-sl-signature": "v1=f36780407a4955d6654c2f70bdf907badcce7486c0e138f0f2cb75c0ef02ed9a",
"x-sl-timestamp": "1764863639",
"x-sl-webhook-delivery-id": "cdc362a5-70f4-4e68-9092-33d446bfe730"
}
payload:
{
"event": "scan.finished",
"timestamp": 1764863639,
"data": {
"scanId": 5,
"orgId": "ba9fa89e-f6dc-427e-ba4f-3fbcf7dc5192",
"appId": "shiftleft-python-demo2_element_SECRETS",
"appName": "shiftleft-python-demo2",
"status": "SUCCESS",
"language": "secrets",
"multilanguageScanId": 5,
"principalAppId": "shiftleft-python-demo2"
}
}
Delivery failure and notifications
If a webhook delivery repeatedly fails and email alerts are enabled, all Super Admins will receive an email notification. The email contains details, such as the organization name, project name, scan ID, and webhook URL.
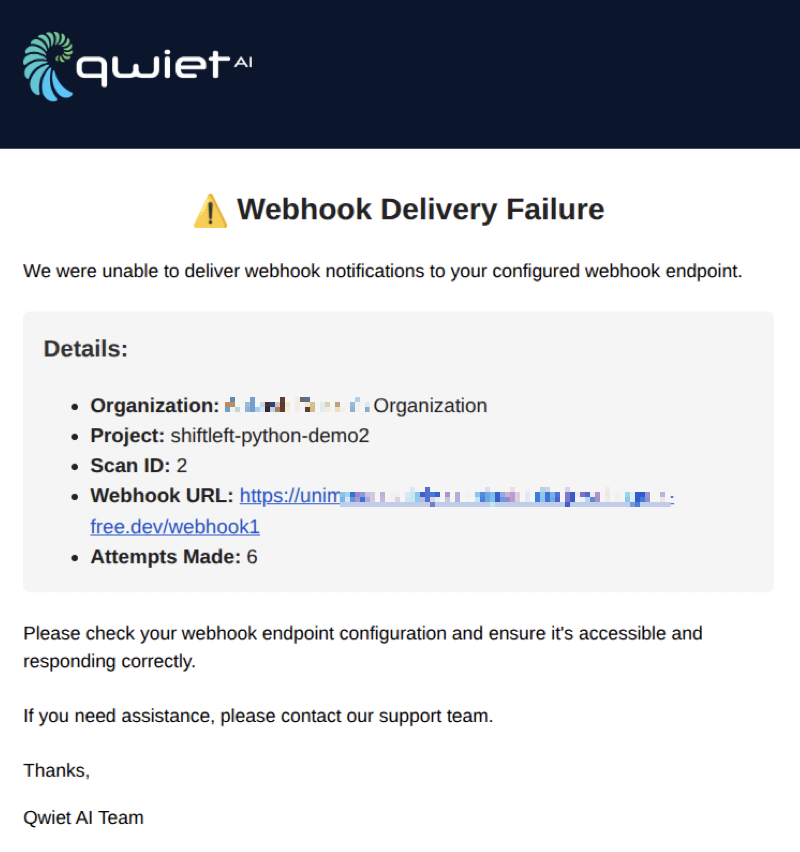
The admin(s) must verify the endpoint availability and ensure that the server responds correctly.